Cryptolocker - Updated News On Cryptolocker Ransomware And Its Effects
What is Cryptolocker?
CryptoLocker infection is a ransomware infection which
was at first seen in 2013. A year after, the gathering of infection analysts
figured out how to check this infection by closing down its primary wholesaler
— the Gameover Zeus Virus. From that point forward, the first undertaking was
however to be dead, yet different CryptoLocker forms have been rising.
Despite the fact that the greater part of new
Cryptolocker variations were outlined by novice programmers, some of variations
have surfaced the web and truly got specialists thinking whether this
ransomware isn't raising from the dead. Tragically, the most recent its
rendition, called Crypt0L0cker, has made heaps of harm PC clients.
Anyway, might it be able to be that the web group's
most noticeably bad dream is turning into a reality in 2017? Contemplations
that Cryptolocker Ransomware is coming back to recover its the most risky ransomware put
have been activated by the way that digital culprits who are in charge of
discharging it may be out of their 3 million dollar benefit.
On the off chance that you believe that you could be
tainted with this infection, don't delay to expel CryptoLocker.
According to a site Lifehacker, Decryptolocker Saves You From the Popular Cryptolocker Ransomware
A propelled type of ransomware that initially
surfaced in September 2013, assaulting people and organizations in the U.K by
landing as a connection in an email that gives off an impression of being a
client grievance. On the off chance that the connection is opened, the
CryptoLocker Trojan steed invades the PC or server and encodes the greater part
of the records on the PC with business review 2048-piece RSA encryption, and
soon thereafter CryptoLocker shows an interest for cash see on the PC.
Otherwise called Crilock, CryptoLocker regularly
requires an installment of 300 Euros through advanced cash installment
techniques, for example, Bitcoins of MoneyPak. The casualty is regularly given
a constrained time span like 72 hours in which to pay the ransomware charge or
hazard for all time losing their information.
On the off chance that the casualty pays the payoff
expense, they can hope to get a decoding key that will reestablish their
information and documents, in spite of the fact that there's no certification
that the digital lawbreakers in charge of the specific variation of
CryptoLocker will respect that guarantee.
CryptoLocker is likewise ready to spread rapidly and
contaminate different PCs by using other bot systems like ZeuS.
Better Encryption Makes CryptoLocker a Threat
For two months, a malevolent bit of malware has
spread to buyer and business PCs, scrambling records and requesting installment
for the way to open the data.
The malware, known as CryptoLocker, or Crilock,
picks up a decent footing in systems when unwary Windows clients open a
connection in an email that has all the earmarks of being a client protest. The
malware contacts a server on the Internet from which it downloads a remarkable
code key and after that encodes the most vital documents on the tainted PC,
showing a message to the client requesting a payoff for the way to open their
information.
Known as ransomware, such projects are not new, but
rather the most recent rendition has increased current standards among the
classification of malignant programming, Nick Levay, boss security officer of
Bit9, told eWEEK. In the current past, ransomware has normally quite recently
utilized an assortment of traps or powerless encryption to bolt a framework,
while CryptoLocker utilizes solid encryption and gives clients a due date to
pay up.
"Previously, the client would go to their go-to
IT fellow and get the stuff tidied up truly brisk," he said. "Be that
as it may, CryptoLocker really has a few teeth."
Ransomware isn't another kind of assault. In 1989, a
program that purportedly showed clients about AIDS and HIV bolted the host
framework when it kept running for the 90th time, scrambling filenames and
registries, and requesting $378 for the open code. Luckily, the encryption
calculation actualized in the infection was amazingly powerless, and the
program reused a similar key, so security firms could work out the open code,
as per a post by Paul Ducklin, head of innovation for security firm Sophos.
"This present century's ransomware has lifted
the bar rather drastically," he composed. "The hooligans scramble
your records utilizing solid encryption with an arbitrarily picked key. At that
point they send the way to themselves, utilizing a protected transfer."
In 2008, a program known as GPCode encoded records
and requested payment for the key. Security firm Kaspersky Lab figured out how
to break the 660-piece RSA key and gave devices to influenced shoppers to
recuperate their information. Before long, the offenders behind GPCode
redesigned the key quality to 1,024 bits, making it significantly more
troublesome, if certainly feasible, to recoup the key.
To begin with recognized by security firms in
September, CryptoLocker enhances that approach, downloading an exceptional key
for every contamination utilizing a server connected to a haphazardly produced
area name. Commonly, utilizing a space age calculation (DGA) makes it more
troublesome for security firms to identify and obstruct the areas utilized by
malware to speak with their criminal administrators, however security firm
OpenDNS has possessed the capacity to ascertain a large number of the space
names and has started blocking them. While such a strategy does not keep a
contamination, it blocks the malware from encoding the influenced PC's
documents.
Read More : ZONEware Ransomware
"We are not doing the customary strategy of
keeping the twofold from descending," Dan Hubbard, boss innovation officer
of OpenDNS, told eWEEK. "By and large, the machine has just run the
parallel, and now it is attempting to signal out and get the encryption key. We
disengage that channel."
The program has likely tainted a great many PCs, as
indicated by information from Kaspersky Lab. More than 2,700 PCs endeavored to
contact the spaces that served up the encryption keys to contaminated
frameworks, as indicated by the firm.
As the primary line of resistance against
ransomware, organizations need to keep great reinforcements, specialists said.
What's more, securing machines with refreshed antivirus projects and preparing
representatives to take a gander at potential phishing email messages can offer
assistance.
While the lawbreakers behind CryptoLocker have
apparently sent keys to those casualties who have paid the payment, security
specialists push that paying up underpins the culprits' model and will prompt
more assaults later on.
Cryptolocker Thieves Likely Making 'Millions' As
Bitcoin Breaks $1,000
It was mid-October when another type of malware
discreetly discovered its direction onto one of the PCs of a private venture in
England, undermined to for all time scramble the greater part of its records,
and after that did just that.IT executive David* had never known about
Cryptolocker, and was perplexed when he got into the workplace that morning and
saw an abnormal fly up with a clock that was tallying down.
It disclosed to him that a huge number of his
organization's records had been encoded, and that he needed to pay a $300
payment to get the unscrambling key to spare them or else they'd remain bolted
until the end of time.
He had no reinforcements, however he additionally
gave no idea to paying up.
David and his organization were one of the early
casualties of Cryptolocker, a sort of malware otherwise called ransomware that
has spread through email crosswise over a great many PCs in the U.K. what's
more, constrained individuals to actually put an incentive on their
information.
Ransomware has been around for a considerable length
of time, however Cryptolocker is abnormally across the board and uses a higher,
business review type of RSA encryption. Today Cryptolocker is advancing into
the United States and gathering significantly higher payoffs in Bitcoin, the
virtual cash which got through $1,000 out of the blue on Wednesday. Much of the
time it's currently requesting 2 Bitcoin as payoff, or more than $2,000.
"I couldn't see how the trojan got in and why
the antivirus didn't stop it," David says. When he checked his antivirus
logs a while later, he could see when the malware had entered, yet there had
been no isolating activity and it was left to spread.
At last, Cryptolocker did precisely as it
undermined, leaving everything encoded and the key erased. The records were not
indispensable and the organization could bear to lose them, yet it was "somewhat
of a hit to my pride," David says. "I didn't consider the installment
strategy since I felt so irate that crooks would profit by that." He wound
up disposing of the malware by moving Windows XP to a past reestablish point to
wipe out the malware, which obviously didn't reestablish the encoded records.
None of his associates would possess up to opening
the phony, messaged connection that let the malware run free. Cryptolocker has
been spreading by means of what resembles true blue business messages,
counterfeit FedEx and UPS following notification, or fake correspondence from
banks and other money related establishments. The messages are focusing on
private companies, and the malware follows Windows documents (70 distinct ones,
for example, PowerPoint and Excel records. In the event that records are shared
on a system, the malware can spread to different machines as well, or USB thumb
drives associated with the tainted PC. The malware that tainted David's
organization was bound to one PC since it was not arranged, and took out .doc,
.xls, .pdf and .mdb records.
Security essayist Brian Krebs has called it a
"fiendish bend on an old trick." It's a great phishing assault, aside
from the malware is modern in moving beyond antivirus programs, tainting PCs by
means of a few surreptitious strides: after casualties get the main spam email,
the connection that a casualty opens downloads a different application, which
downloads malware that at last downloads Cryptolocker, as indicated by Uttang
Dawda of security programming firm FireEye, who has been considering the malware
throughout the most recent month.
Bitcoin is vital to Cryptolocker's continuation
The cash is anonymized and means deliver installments can't be followed —
however it was additionally an issue for Cryptolocker at first. As per Krebs,
beginning casualties of Cryptolocker like David were eager to pay the payment
however couldn't on the grounds that they didn't know how to make installments
through Bitcoin or Moneypak, which was another type of acknowledged
installment.
Not long ago, the culprits changed tack, giving
casualties another opportunity to pay the payment. The principal emancipate
requests began at $100, at that point rose to $300, and are presently commonly
at 2 Bitcoin (generally $2,000 today). The additional opportunity deliver rises
five crease to 10 Bitcoin. The controllers even set up a client benefit include
on Tor, where casualties would more be able to effortlessly pay up. The
interesting, easy to understand site on the anonymized organize says that
"clients" just need to transfer one of their encoded records to get a
request number, to then "buy private key and decrypter for
documents."
Looking forward, the Cryptolocker cheats would need
to do some major redoing on the off chance that they needed the malware to
spread to cell phones, says FireEye's Uttang, yet it's inside the domains of
probability as the malware keeps on spreading topographically.




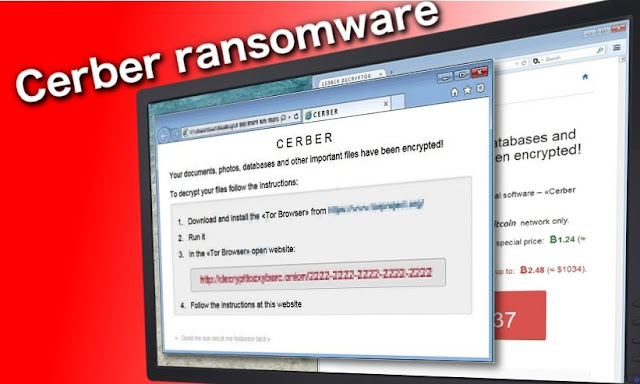
Cryptolocker - Updated News On Cryptolocker Ransomware And Its Effects >>>>> Download Now
ReplyDelete>>>>> Download Full
Cryptolocker - Updated News On Cryptolocker Ransomware And Its Effects >>>>> Download LINK
>>>>> Download Now
Cryptolocker - Updated News On Cryptolocker Ransomware And Its Effects >>>>> Download Full
>>>>> Download LINK ZC